
HPC-T-Annotator

Architecture design
The logic behind the application can be summarized simply as follows: the user, who intends to perform the alignment process, provides HPC-T-Annotator with the input Multi-FASTA file. This file, which would typically be the analyzed file used with traditional alignment software, contains the sequences of interest. In order to expedite the alignment process, HPC-T-Annotator employs a distributed approach where the sequences within the input file are distributed and annotated separately and independently.
This parallelization strategy enables us to achieve significant reductions in alignment time. By leveraging the power of distributed computing, HPC-T-Annotator harnesses the computational resources of an HPC cluster, allowing multiple alignment instances to be executed simultaneously. Each alignment instance compares a subset of sequences from the input file to a sequence database, inferring their functions based on homology. The results of these separate alignments are then consolidated to generate the final alignment output.
This approach enables researchers to obtain comprehensive and accurate annotation results within significantly shorter timeframes, enhancing their ability to analyze and understand the functional roles of the expressed genes in the specific organism of interest.
Complete workflow diagram of parallel processing of HPC-T-Annotator
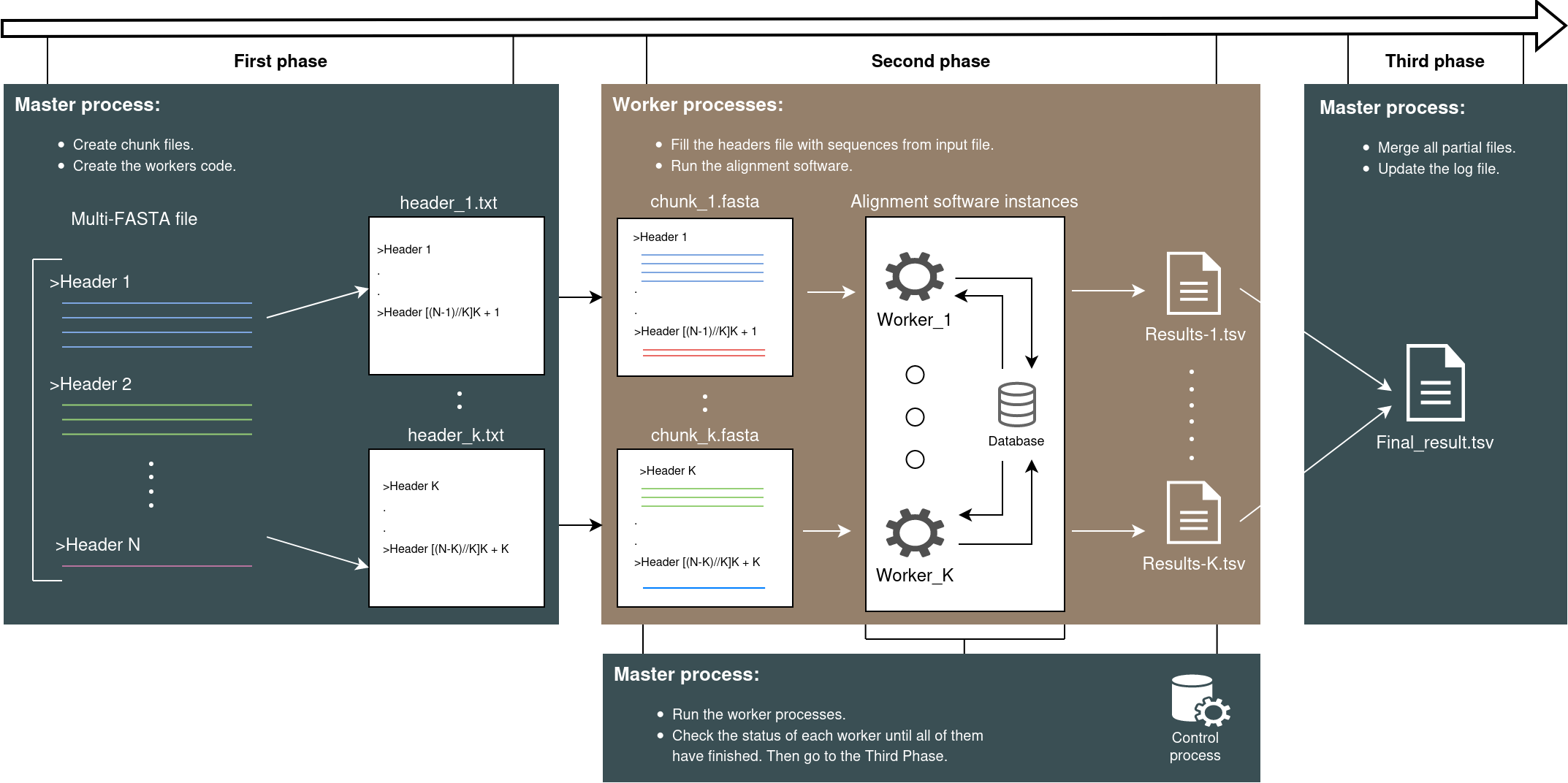
Figure: Workflow diagram of parallel processing of HPC-T-Annotator.
Phase 1: Splitting the Input File
As a first step, the input file provided by the user (containing the sequences on which to perform the homology annotation process in Multi-FASTA format) is split into multiple partial files (on which alignment will be performed in parallel mode), each containing a portion of the sequences that were initially in the original file. Each process will then be assigned a certain number of sequences on which to perform the alignment.
The scattering algorithm used in the application is the Cyclic-Distribution, which consists of the cyclic assignment of sequences within the input file. This ensures a proper load balancing, distributing the workload effectively.
Phase 2: Performing the Alignment
After the splitting phase, where the initial files are divided into smaller parts, the subsequent step involves aligning the different sequences contained within these partial files. This alignment process is crucial for identifying similarities and relationships between the sequences, providing valuable insights into their functions and evolutionary origins.
To accomplish this alignment, each process initiates an instance of the selected alignment software, such as BLAST or Diamond. These software tools employ sophisticated algorithms and databases to compare and match the sequences against each other. By utilizing parallel processing, multiple instances of the alignment software are launched simultaneously, allowing for faster and more efficient analysis.
As the alignment software runs, it generates partial results for each process or instance involved in the alignment. These partial results represent the individual findings and matches discovered by each instance of the software. Combining these partial results from all the processes leads to a comprehensive overview of the sequence alignments, highlighting the shared characteristics and differences among them.
Phase 3: Merging the Results
Finally, after the completion of all computations, the master process gathers the outputs from the sub-files and proceeds with a merging operation. This crucial merging step combines all the alignment results obtained from the individual files, consolidating them into a single file in a tab-separated value (tsv) format. By bringing together the alignments from different parts of the data, this unified file not only provides a comprehensive overview of the analysis but also facilitates researchers in efficiently accessing and interpreting the complete set of alignment results. Moreover, this streamlined approach ensures the seamless integration of information, ultimately simplifying further downstream analysis and enhancing overall productivity.